There are many reasons why your 3D prints can be unsuccessful, but the most common one is using the wrong filament. As someone who’s spent hundreds of hours studying and creating 3D models, I’ve went through a lot of trial and error to figure out which 3D filaments are suitable for what type of printing. Every filament has its own distinct advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for printing some types of 3D prints, while unsuitable for others. So whether you’re new to 3D printing and want to save yourself the time and money finding the most suitable filament, or you’re an advanced user who’s looking to experiment, here’s what you need to know about the most commonly used 3D filaments before you decide which one is right for you.

source: all3dp.com
ABS 3D Printer Filament
ABS is one of the most popular 3D printing filaments, as it’s affordable, great for printing, durable and features tough parts that can withstand high temperatures. It’s one of the first plastics used for industrial 3D printing, and it’s known for its impact resistance and toughness, which enables you to print parts that will hold up extreme wear and tear. In fact, LEGO blocks are made from ABS for the same reasons. Its ability to withstand high temperatures before it starts deforming makes it a great choice for high temperature and outdoor applications. When using this 3D filament, it’s important to have proper ventilation, as the material can release a slight odour. Further, ABS usually contracts as it cools, so controlling the temperature of the build volume and the part inside can be beneficial. Printing ABS requires a heated chamber or heated bed, and parts made of ABS may shrink, which can lead to dimensional inaccuracy.
source: 3devo.com
PLA 3D Printer Filament
PLA is another popular type of filament, simply because it’s affordable, easy to use and offers dimensional accuracy. Also known as Polylactic Acid, it’s the default filament of choice for many extrusion-based 3D printers as it doesn’t require a heated bed, meaning it can be printed at a low temperature. Further, it’s the ideal first material to use when you’re learning for the aforementioned reasons. Plus, it’s one of the most environmentally friendly options available today. It’s derived from crops such as sugarcane and corn, making it biodegradable. However, this also means that it’s not suitable for outdoor applications. It has a low heat resistance, and it can get brittle and break.
Nylon 3D Printer Filament
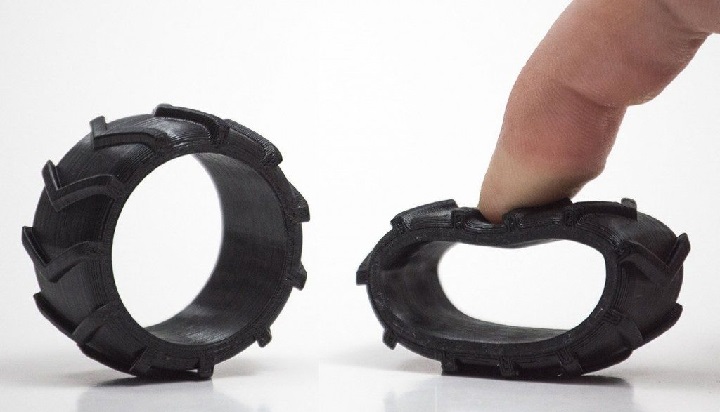
Nylon filament is a semi-flexible and tough material that boasts high abrasion and impact resistance, making it ideal for printing durable parts. Nylon 3D printer filament is especially popular in the plastics industry, but printing with it will require temperatures of about 250°C. Another challenge with nylon filaments is that they’re hygroscopic, meaning they will readily absorb moisture. If that happens, the resulting print may have several quality issues. That being said, storing nylon filament properly is extremely important and it requires special care.

source: simplify3d.com
Flexible 3D Printer Filament
Flexible filaments, also known as TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers), are known for their elasticity, allowing the material to bend and stretch easily. These filaments are a blend of rubber and hard plastic. There are a few different types of TPE, with TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) being the most popular one in 3D printing. Sometimes, the terms TPE and TPU are interchangeable, along with some popular brand names like Ninjaflex. The level of elasticity depends on the chemical formulation and the type of TPE used by the manufacturers. For instance, some flexible filaments can be semi-flexible, like car tyres, while others can be fully flexible, like rubber bands.
PET 3D Printer Filament
PET filaments are known for their smooth surface finish, ease of printability and water resistance. PET is Polyethylene Terephthalate, whereas PETG is a Glycol Modified version of PET. PET is used to manufacture water bottles, and it’s a semi-rigid material that boasts decent impact resistance properties. However, it has a soft surface which makes it prone to wear. But PET boasts great thermal characteristics, enabling the plastic to cool without warping. These are a couple of different variations of PET, including PETG, PETT and PETE.

source: 3dprintingindustry.com
ASA 3D Printer Filament
ASA is a popular alternative to ABS plastic, and it’s great for outdoor applications due to its high temperature, UV and impact resistance properties. Also known as Acrylic Styrene Acrylonitrile, ASA was originally made as an alternative to ABS with improved UV resistance, by using a different type of rubber. However, ASA is also more difficult to print. Besides the improved UV resistance, most of its other characteristics are the same as those in ABS. Warping is still something you need to account for, as well as the potentially toxic fumes that it emits when printing. ASA is also more expensive, and requires high extruder temperatures.



